soil permeability test 50 ml of water|typical permeability of soils : specialty store Permeability tests can be performed with the sample from 0% to 100% relative density, as required. After compacting thin layers of the prepared granular soil sample in the permeameter, a special sliding-weight compaction hammer or . WEBАвиатор Пин Ап: Часто задаваемые вопросы. Узнайте о практике онлайн-гемблинга у Авиатора Пин Ап и получите полезные советы и хитрости этого профессионала.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Obtenha robux moedas Roupa grátis em ROBLOX com a ajuda do nosso gerador. Como você já viu, nosso gerador de recursos é muito fácil de usar. Você pode usá-lo para melhorar a jogabilidade de qualquer .
Soil permeability (hydraulic conductivity) is the rate at which water flows through soil materials. It is an essential characteristic across a broad spectrum of engineering and earth-science disciplines. See morePermeability tests can be performed with the sample from 0% to 100% relative density, as required. After compacting thin layers of the prepared granular soil sample in the permeameter, a special sliding-weight compaction hammer or . Field Testing Methods, such as percolation tests and pump tests, can assess soil permeability for different types of soils according to standards like ISO 17892 or ASTM D5084. .
Portable digital Powder Moisture Meter convenience store
PERMEABILITY TEST METHOD A. SCOPE. The permeability test is a measure of the rate of the flow of water through soil. In this test, water is forced by a known constant pressure through a . The soil permeability chart is an accessible, simple way to see the typical values of permeability for different soil types. The constant head permeability method determines permeable soils like sand. This test .Permeability of a coarse grained soil can be determined by a constant head permeability test (AS1289.6.7.1-2001; ASTM D2434), and in a fine grained soil, falling head permeability test .The objective of constant head permeability test is to determine the coefficient of permeability of a soil. Coefficient of permeability helps in solving issues related to: Yield of water bearing strata. Stability of earthen dams. Embankments of .
Soil permeability is the quality of a soil enabling it to transmit air or water through the soil pores. Texture, structure, cracking, and the amount of organic matter influence the .
Soil permeability is usually represented by the coefficient of permeability (k), where k is the rate of flow of water per unit area of soil when under a unit hydraulic gradient. TPermeability, or hydraulic conductivity, refers . Soils with high permeability are typically loose, while those with low permeability are tight or compacted. Compacted soil significantly reduces permeability. Soil structure is also a significant factor influencing soil permeability (Fig. 8.4). Granular structure, characterized by interconnected macropores, facilitates easy water movement.Overview of Laboratory Methods Testing Soil Permeability. The most accurate permeability measurement technique involves laboratory constant head testing per ASTM D2434 standards using specialty columnar chambers allowing .
the effects of water in the soil on its engineering properties, and . Laboratory Testing 2. Field Testing 3. Empirical Equations 1. . Discharge and seepage velocity for a permeability of 0.1 cm/s and a porosity of 50%. 1m 4m 1m 4m A Datum Example (2nd midterm exam Fall 38-39) Elevation Head Pressure HeadFIELD MANUAL 110 Table 17-1.—A glossary of abbreviations and definitions used in permeability calculations K = Coefficient of permeability in feet (meters) per year under a unit gradient. Q = Steady flow into the well in ft3/sec [m3/sec]. H = The effective head of water in the well in feet (m). For packer tests, determining the effective head is definedThe attached figure shows the soil sample prepared and setup for constant head permeability test. If the permeability of the soil is 4.5 x 10 what is the required time to collect 100 ml of outflow water under the steady state condition? cm/sec 50 cm Soil in the pipe with internal diameter 10 cm Outflow collection 50 cm 90 cm 350 10 cm Datum- a. 493 min b. 283 min c. .The attached figure shows the soil sample prepared and setup for constant head permeability test. If the permeability of the soil is 4.5 x 10-3 cm/sec, what is the required time to collect 100 ml of outflow water under the steady state condition? 40 cm Soil in the pipe with internal diameter 20 cm Outflow collection 50 cm 40⁰ 90 cm -Datum- 10 cm
a) A constant head permeability test was carried out on a cylindrical sample of sand of 10 cm diameter and 15 cm height. 200 cm3 of water was collected in 2.25 min under a head of 30 cm. Compute the hydraulic conductivity in m/sec. b) Calculate the hydraulic conductivity of a soil sample 6 cm in height and 50 cm2 crosssectional area if 430 mL .
Problem: For a constant laboratory permeability test on a fine sand, the following data are given: Length of specimen - 16 cm Diameter of specimen - 9.6 cm Constant head difference - 50 cm Volume of water collected in 4 min - 420 cc Void ratio of the soil specimen - 0.55 A.) Determine the hydraulic conductivity of the soil in cm/sec B .3.1.1 Continuity of flow with no soil volume change during a test, 3.1.2 Flow with the soil voids saturated with water and no air bubbles in the soil voids, 3.1.3 Flow in the steady state with no changes in hydraulic gradient, and 3.1.4 Direct proportionality of velocity of flow with hydrau-lic gradients below certain values, at which .The attached figure shows the soil sample prepared and setup for constant head permeability test. When the flow through sample reached the steady state conditions, 50 ml outflow measured for 10 sec. . 50 ml outflow measured for 10 sec. What is the coefficient of the permeability of the so 40 cm Soil in the pipe with internal diameter 20 cm .
Question: 1 Problem: During a constant head permeability test on a sample of sand, 150 cu.cm. of water were collected in 2 minutes. The sample had a length of 10 cm. and a diameter of 5.08 cm. The head was maintained at 20 cm. a) Compute the .
From the constant head permeability test, the following values are given: Void ratio of specimen 0.46 Length of soil sample 450 mm Constant head difference 700 mm Water collected in a period of 180 seconds Cross-sectional area of soil sample 3.54 x 10-4 m³ 2.26 x 10-3 m² a.)The head difference between manometer levels was 49 mm during the test, and the water temperature was 20°C. If it took 152 s for 500 mL of water to discharge, determine the coefficient of permeability of the sample. Water supply AH Overflow Cross sectional area A .
the permeability of systems of soil and fabric in direct contact ( 5-8). However, to provide a simple . geotextiles in a water-permeability test. With moderate gradients the flow rate is very high in a constant-head device. This requires large volumes . The constant head permeability test is usually preferred for sandy soils and the variable head permeability test for silty and clayey soils. A separate constant head method for granular soils has been recommended by . 5.13 - Calculate the coefficient of permeability of a soil sample, 6 cm in height and 50 cm2 in cross sectional area, if a quantity of water equal to 430 ml .Information obtained from a particle size analysis can be used to predict soil-water movement if a permeability test is not available. Objective. . Place 50 g of fine soil in a beaker, add 125 mL of the dispersing agent (sodium .
The attached figure shows the soil sample and setup for constant head permeability test. If the permeability of the soil is 4.5 X 10^-3 cm/sec, what is the required time to collect 100 ml of outflow water the steady state condition? Soil permeability is the quality of a soil enabling it to transmit air or water through the soil pores. Texture, structure, cracking, and the amount of organic matter influence the permeability. 9.8: Soil Permeability - Geosciences LibreTextsThe figure below shows a constant head test setup used to measure the permeability of a sandy soil. The water levels are also shown. The soil sample is 20 cm in length, and 5 cm in diameter. During a period of 10 minutes, 100 ml of water was collected in the container. The soil was saturated, and the water flow in the soil was laminar flow. (1 .ADVERTISEMENTS: Determination of Coefficient of Permeability in Laboratory: 1. Constant Head Permeability Test (Coarse Grained): Water flows from the overhead tank consisting of three tubes – The inlet tube, the over-flow tube and the outlet tube. The constant hydraulic gradient i causing the flow is the head h (i.e., difference in water levels of the [.]
Portable Digital Food Moisture Meter convenience store
The water levels are also shown. The soil specimen is 20 cm in length, and 5 cm in diameter. During a period of 15 minutes, 200 ml of water was collected in the effluent container. During the test, the soil was saturated, and the water flow in the soil was laminarWhen you take an undisturbed sample to a testing laboratory, to measure permeability, a column of soil is placed under specific conditions such as water saturation and constant head of water. The result will be given to you either as a permeability rate (see Table 15), or as a coefficient of permeability (see Table 16).• Plan an economical testing program. • Extend test results to additional explorations. For final design of important structures, visual soil classification must be supplemented by laboratory tests to determine soil engineering properties such as permeability, shear strength, and compressibility under expected field conditions.1. Pour 100 mL of water into your cup and draw a line where the water comes up to. Write 100 mL in the total volume column on your data sheet. Dump out the water. 2. Fill the cup with the first soil sample up to the line you drew. 3. Using your graduated cylinder, slowly and carefully pour water into the cup until the water reaches the top of .
Permeability is the ease with which water can flow through the soils. There are numerous methods through which we can measure the permeability of a soil in the field or of a representative sample in the laboratory. In the laboratory we employ two methods. 1. Constant Head Permeability Test. 2. Variable Head or Falling Head Permeability TestTherefore, investigation on the permeability of granular soil under such confining stress condition becomes mandatory. In general, permeability test on the soil in a laboratory is per-formed either by employing rigid wall permeameter, RWP, (Chapuis 1990; Steiakakis et al. 2012)orflexiblewall permeameter, FWP, (Komine 2004; Dafalla et al. 2015).
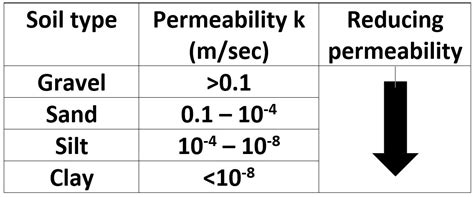
typical permeability values of soil
Portable dried fruits and vegetables Moisture Meter convenience store
typical permeability of soils
soil permeability test procedure
Resultado da Emissão da Credencial (primeiro cadastro) Renovação da Credencial (90 dias antes do vencimento) Consulta de saldo e recarga de crédito (restaurante .
soil permeability test 50 ml of water|typical permeability of soils